Layouts
A layout is UI that is shared between multiple pages. On navigation, layouts preserve state, remain interactive, and do not re-render. Layouts can also be nested.
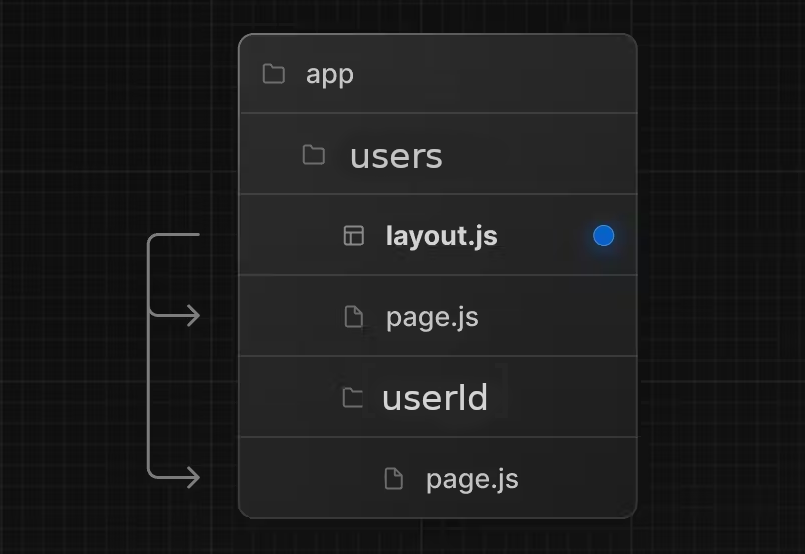
You can define a layout by default exporting a React component from a layout.js file on users folder. The component should accept a
children prop that will be populated with a child layout (if it exists) or a child page during rendering.
import styles from './users.module.css'
export default function UsersLayout({
children, // will be a page or nested layout
}) {
return (
<section>
<nav className={styles.nav}>
users page
</nav>
{children}
</section>
)
}
Root Layout
import './global.css'
export default function RootLayout({children}) {
return (
<html lang="en">
<body>
<nav>Root layout</nav>
{children}
</body>
</html>
)
}
- A
layout.jsandpage.jsfile can be defined in the same folder. The layout will wrap the page.- The
top-mostlayout is called the Root Layout. Thisrequiredlayout is shared acrossall pagesin an application. Root layoutsmust contain html and bodytags.- Any route segment can optionally define its
own Layout. These layouts will be shared across all pages in that segment.- Layouts in a route are
nestedby default. Each parent layout wraps child layouts below it using the React children prop.Passing databetween a parent layout and its children is not possible. However, you can fetch the same data in a route more than once, and React will automaticallydedupethe requests without affecting performance.- Only the
root layoutcan contain<html>and<body>tags.
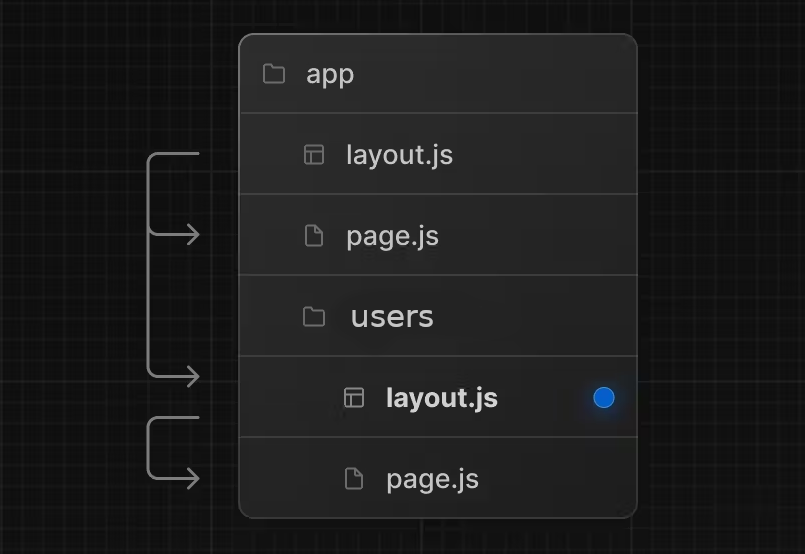
Nesting Layouts
Layouts defined inside a folder (e.g. app/users/layout.js) apply to specific route segments (e.g.
mywebsite.com/users) and render when those segments are active. By default, layouts in the file hierarchy
are nested,
which means they wrap child layouts via their children prop.
💡 We have a similar concept that is called
template, it has a little difference in comparison with layout.